As part of my EECE7150 Autonomous Field Robotics course's project at Northeastern University, I developed a camera–LiDAR temporal calibration method based on geometric and visual edge alignment across sensors. Additionaly, I estimated sub-frame time offsets via robust optimization and validated alignment using LiDAR-to-image projection overlays.
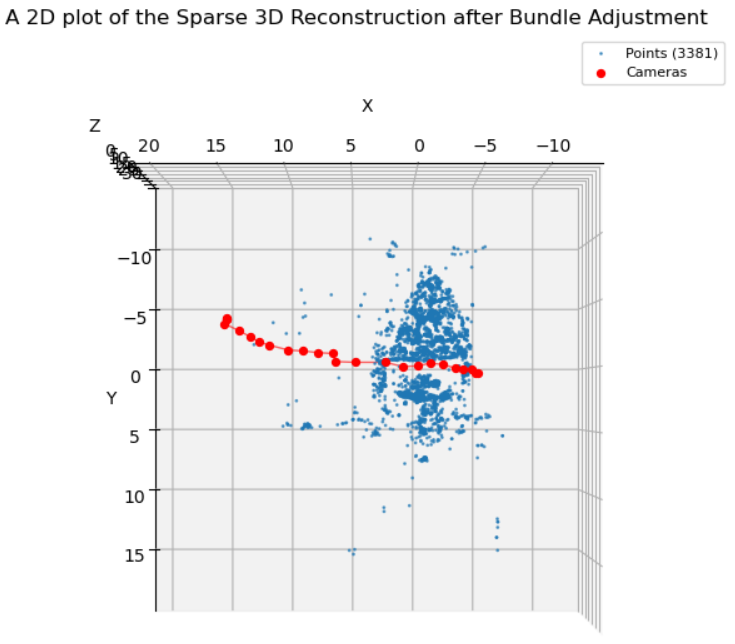
As part of my EECE7150 Autonomous Field Robotics course's project at Northeastern University, I developed an end-to-end Structure-from-Motion pipeline from scratch to estimate camera poses and reconstruct sparse 3D structure from multi-view images. I aslo applied global bundle adjustment with GTSAM to significantly reduce reprojection error and improve trajectory consistency.

As part of my EECE5550 Mobile Robotics course's project at Northeastern University, I reproduced a simplified, CPU-only version of the implementation of the 3D-BBS (Branch-and-Bound Scan Matching) algorithm for global localization using LiDAR data. This project aligns 3D LiDAR scans to a voxelized map by exhaustively searching a 4D pose space (x, y, z, yaw) and scoring candidates using voxel occupancy overlap. This algorithm was originally proposed in the 3D-BBS: Global Localization for 3D Point Cloud Scan Matching Using Branch-and-Bound paper.
As part of our ME5659 Control Systems Course course's project at Northeastern University, we focused on designing and comparing three different controllers: PID, Lead-Lag, and LQR, for regulating the velocity of a Toyota Camry XLE under aerodynamic and rolling resistance forces.

Created custom ROS 2 messages and drivers for GPS and IMU sensors and collected data using the NUANCE autonomous car provided by Northeastern University. Analyzed the IMU's noise characteristics through Allan Variance and calibrated magnetometer by correcting hard and soft iron distortions and error compensation in IMU and GPS data. Compensated for accelerometer bias to estimate the vehicle’s forward velocity, and fused the yaw angle computed from the gyroscope and magnetometer data using a complementary filter to estimate heading for Dead Reckoning with IMU.
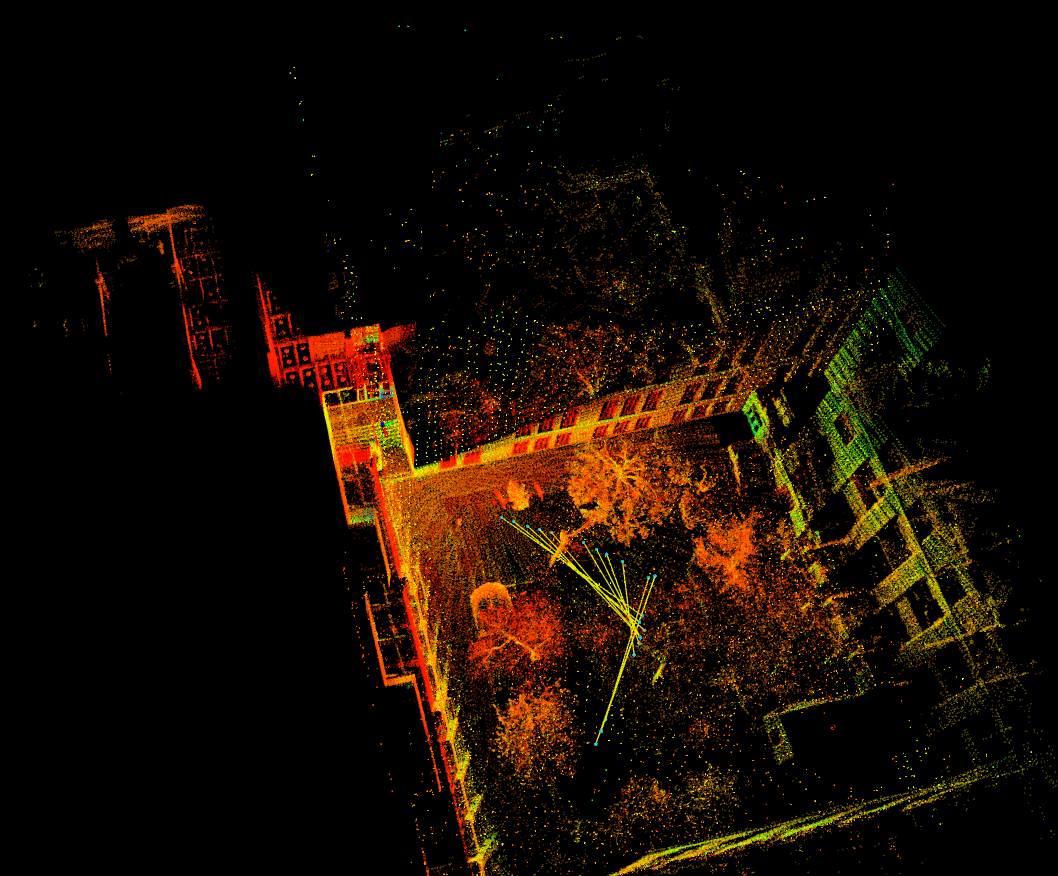
Collected data in NUANCE autonomous car using the Ouster 3D lidar, VectorNav (VN-100) IMU, and GPS sensors while driving around the streets of Boston. Tested FAST-LIO, FAST-LIO LC, and LIO-SAM on standard datasets as well as on our data, displayed the results for FAST-LIO and FAST-LIO LC, and highlighted challenges faced in LIO-SAM. Compared the results obtained from FAST-LIO and FAST-LIO LC to highlight the advantages of Loop Closure in SLAM algorithms.
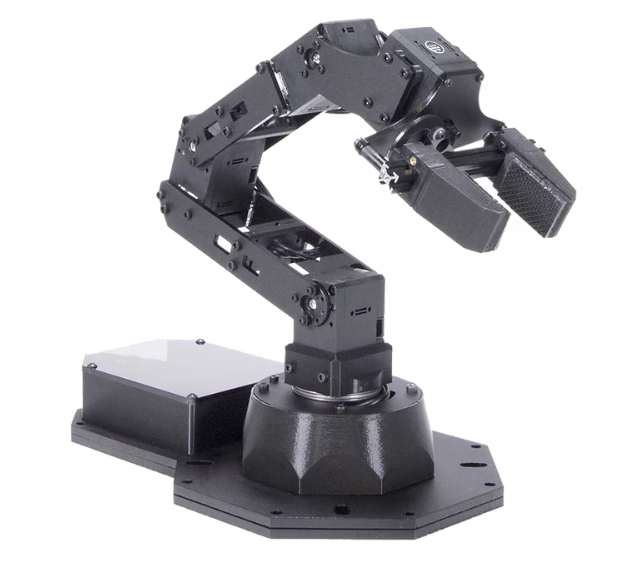

Performed pick-and-place task for a cylindrical payload using the PincherX100 robot manipulator. Employed concepts such as forward kinematics and Inverse Kinematics and designed a Trajectory Planner for the end-effector of the arm. Implemented obstacle avoidance along with the normal pick-and-place function of the arm.
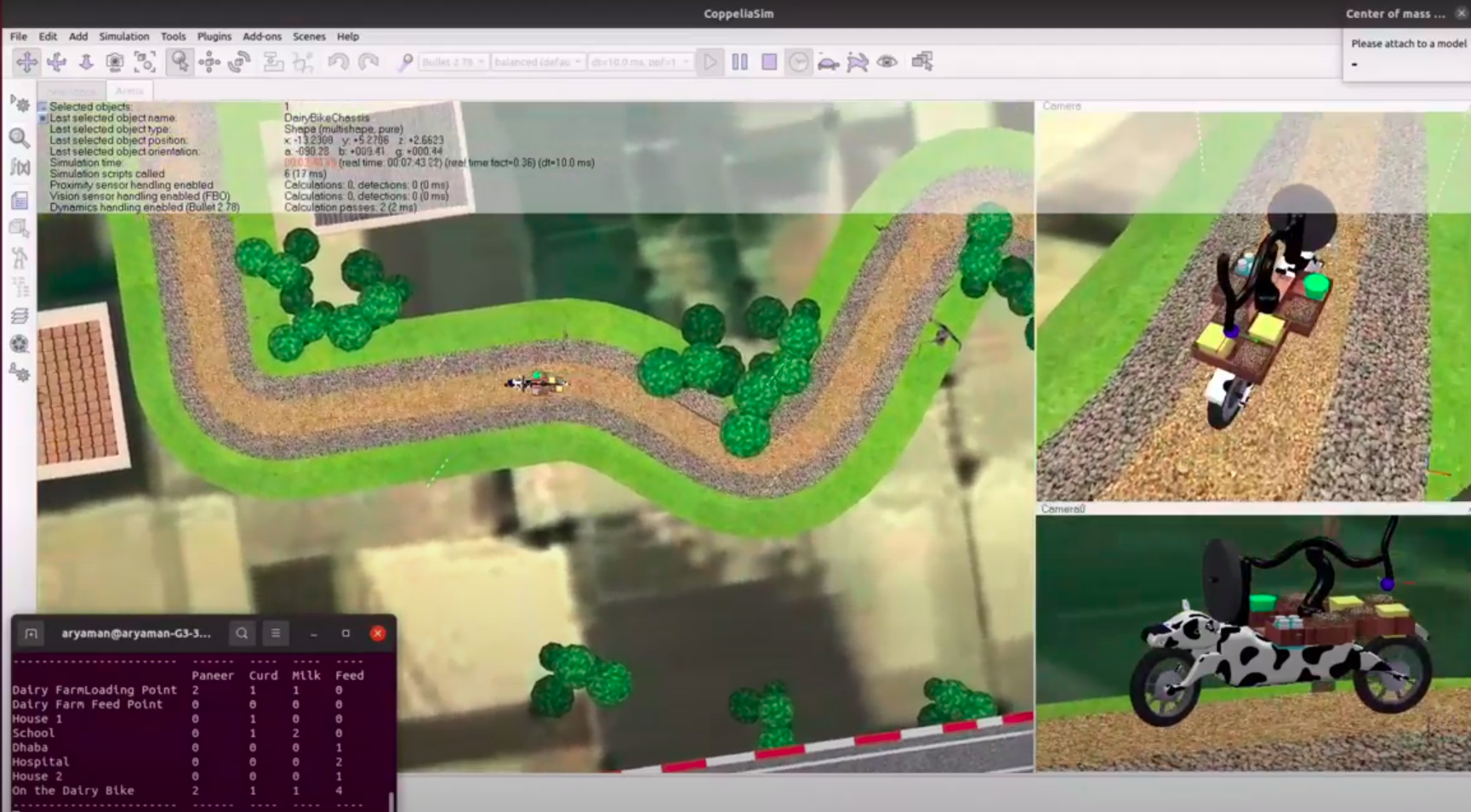
Secured 3rd place in the Eyantra Robotics Competition 2021 - 2022. Developed a two wheeled bike which uses Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) to balance itself. Used State-Space equations and Euler Lagrange method to mathematically model the bike. Designed a custom 4-DOF arm to pick and place the dairy products. Navigated the bike through the arena overcoming various obstacles placed at different points in the entire arena.
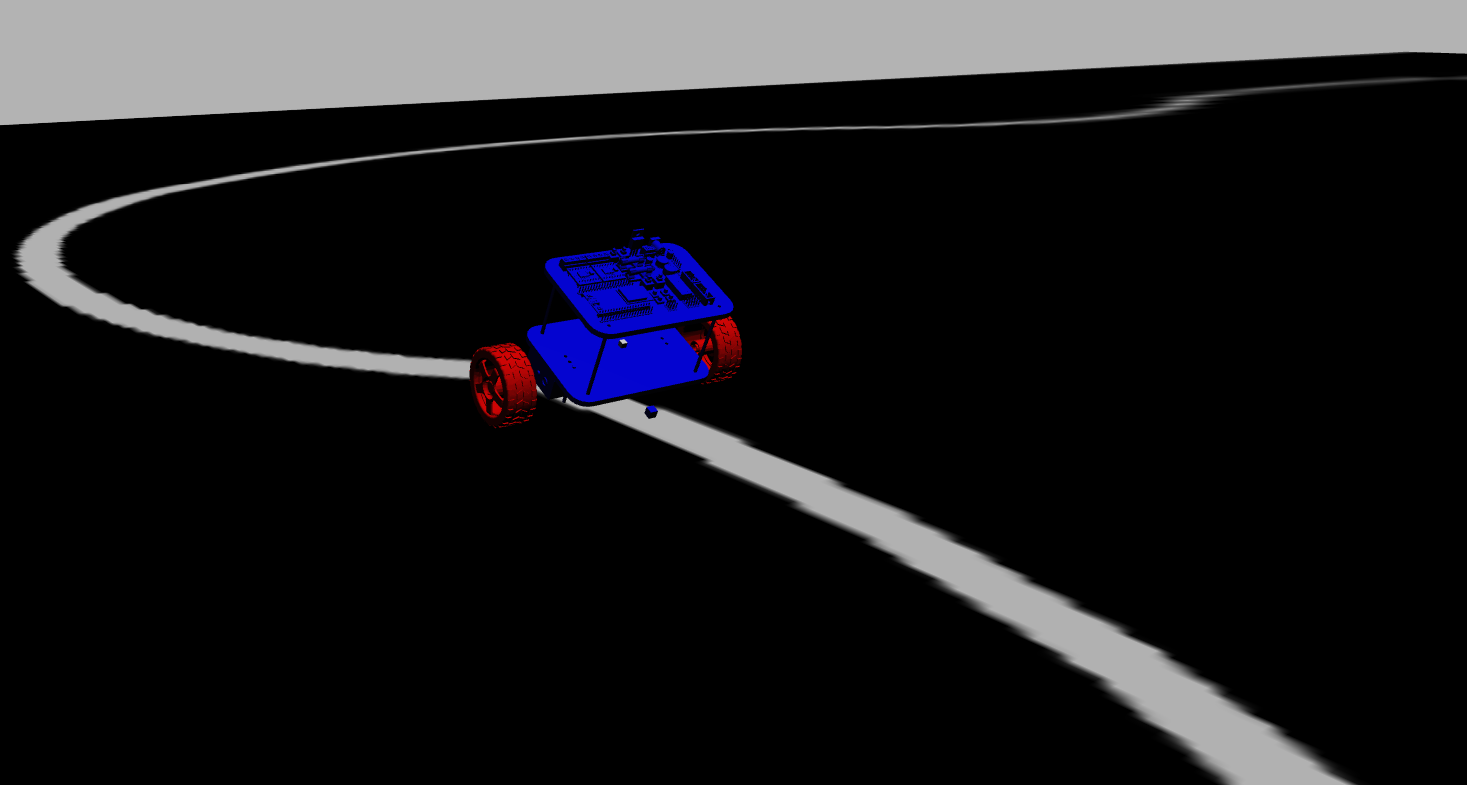
Designed a two-wheeled robot and wrote self-balancing and line-following algorithms for it using Propotional Integral Derivative (PID) controller. Solidworks was used to design the robot. Used ROS 2 Foxy and Gazebo to simulate it.
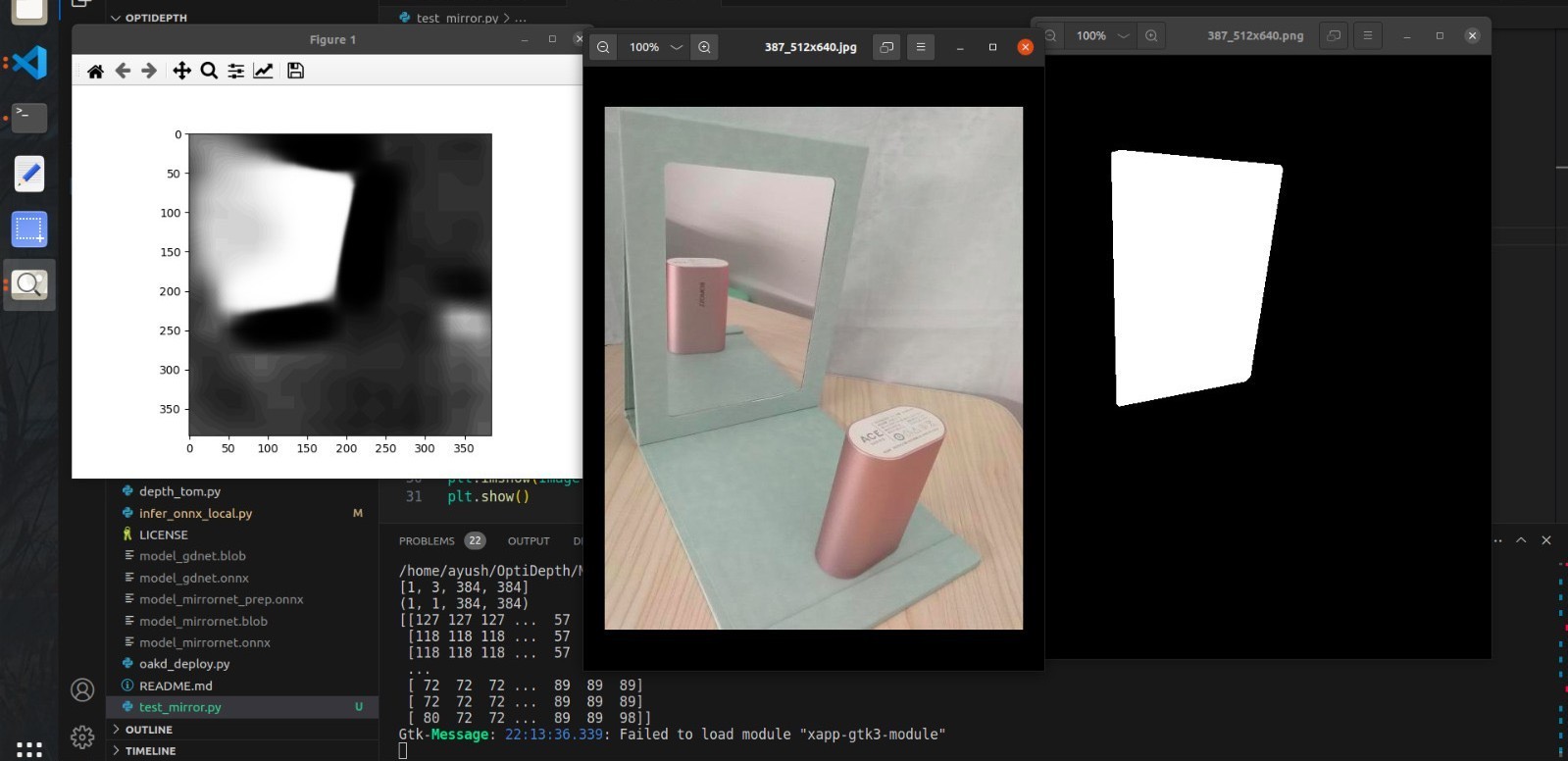
Performed accelerated depth estimation on reflective and transparent surfaces through quantization optimization.
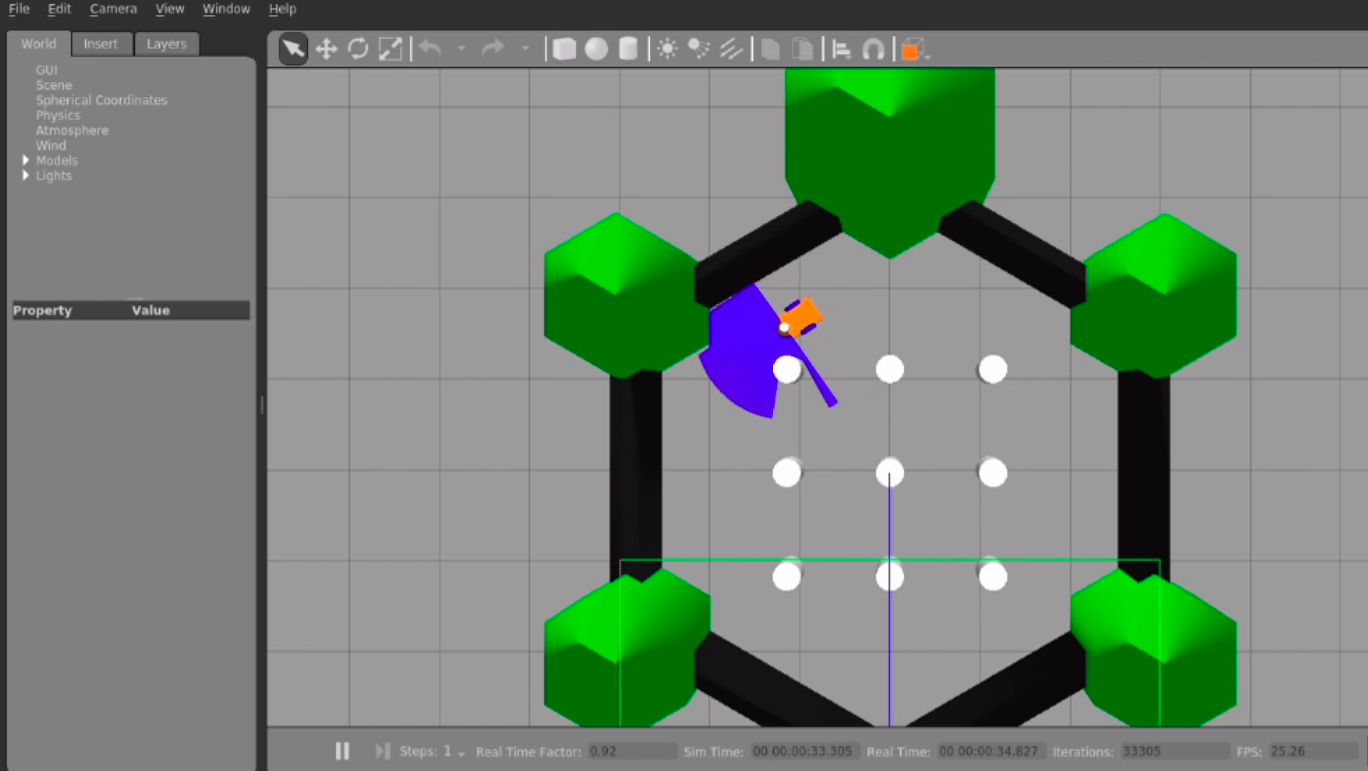
Implemented an obstacle avoidance algorithm on a differential drive robot and simulated it using ROS Noetic and Gazebo.
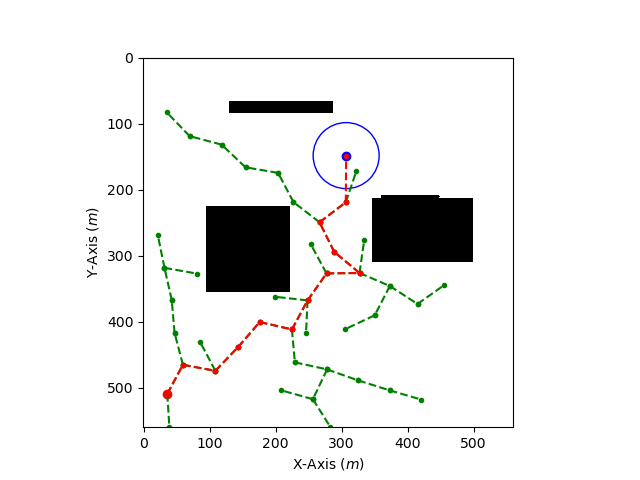
Implemented the Rapidly Exploring Random Trees (RRT) Algorithm from scratch using Object-Oriented Programming (OOPs) in Python. Created a simulation to visualize the working of the algorithm using Matplotlib. Made some of the parameters dynamic, such as having random start and goal positions each time, and taking the number of obstacles as input from the user within a specific range. Also, devised some parameters, such as the number of iterations required, the number of final waypoints needed, and the total distance traversed, to evaluate the performance of the algorithm.
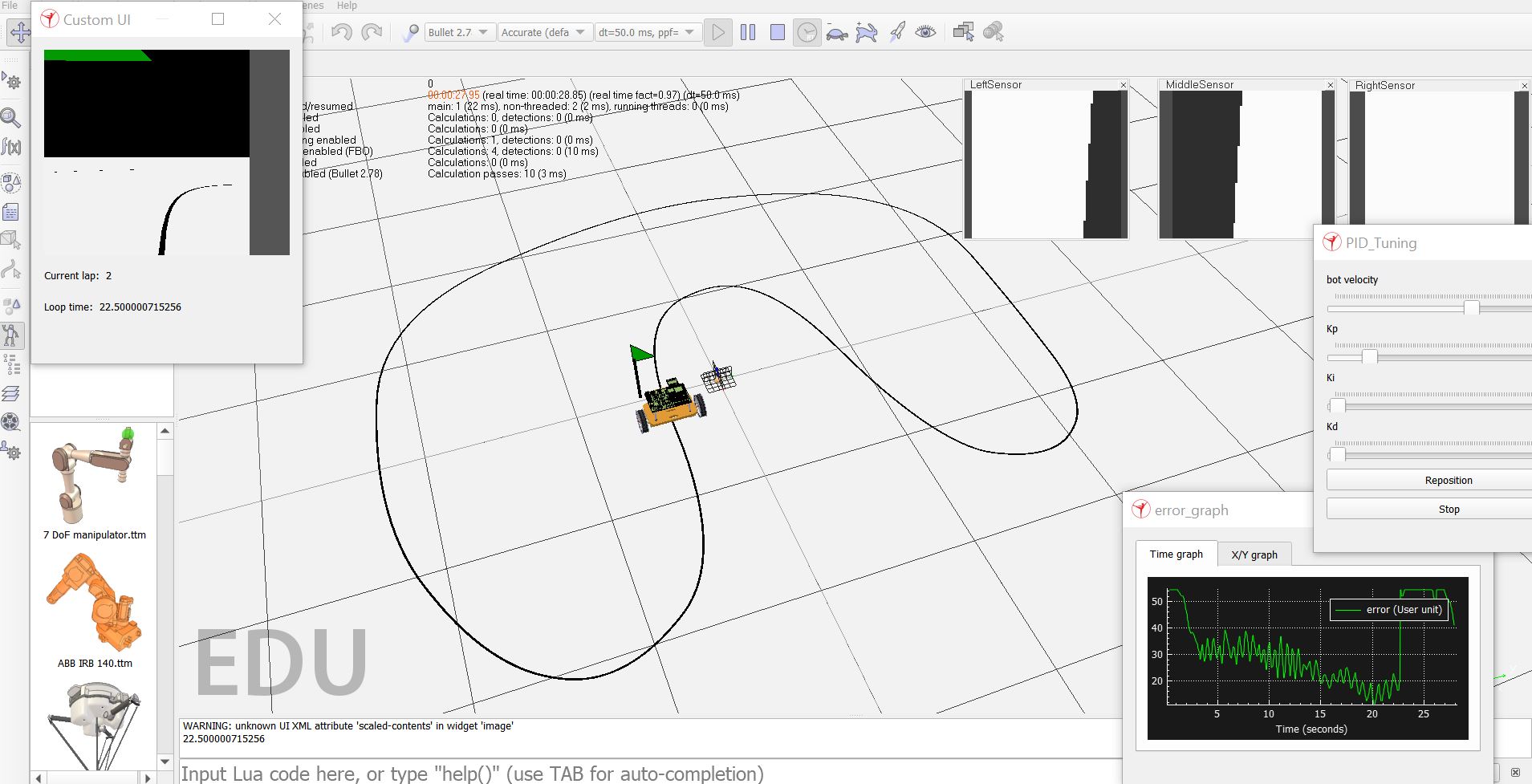
Contributed to enhancing the existing simulations in this repository as well as creating the new self-balancing task. These CoppeliaSim simulations are used as assignments to teach first-year students various concepts like Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller tuning, line-following, self-balancing, and maze-solving, as a part of the WallE workshop conducted by the members of the Society Of Robotics And Automation (SRA), VJTI.